Vuex
2023年5月8日
概念
状态管理模式,简单的讲,将多个组件共享的变量全部存储在一个对象里面。
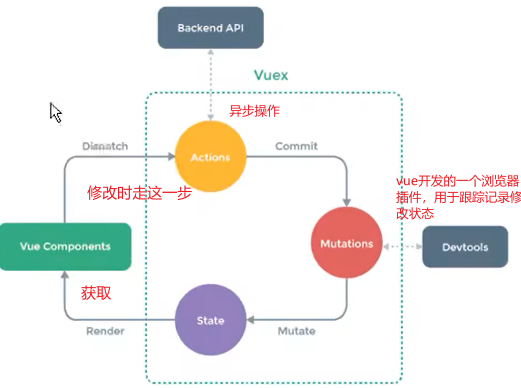
简易实现
所有的组件都继承Vue的源型。(如Vue.prototype.shareObj = shareObj即所有的组件都可访问该变量)这样也可以实现状态管理功能,但是缺乏响应式。
需要管理的状态
多个界面共享的状态,如
- 用户登录状态、名称、头像、地理位置等。
- 商品收藏、购物车
基本步骤
- 安装插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
- 创建对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
getters: {},
modules: {}
})
// 导出store独享
export default store
- 挂载Vue实例
// main.js
import store from './store'
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
简单使用
计数器案例
创建store文件下的index.js
import Vuex from 'vuex' import Vue from 'vue' Vue.use(Vuex) const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { increment(state) { state.count++ }, decrement(state) { state.count-- } } }) export default store使用Vuex的count
- 获取:
$store.state.count - 修改:
this.$store.commit('mutation中的方法')通过提交mutation的方式,而非直接改变,因为Vuex可以更明确的追踪状态的变化
// App.vue <template> <div id='app'> <p>{{ $store.state.count }}</p> <button @click="addition"></button> <button @click="subtraction"></button> </div> </template> <script> export default { ... methods: { addition() { this.$store.commit('increment') }, subtraction() { this.$store.commit('decrement') } } } </script>- 获取:
核心概念
State单一状态树
- 如果你的状态信息是保存到多个Store对象中的,那么之后的管理和维护等等都会变得特别困难。
- 所以Vuex也使用了单一状态树来管理应用层级的全部状态。
- 单一状态树能够让我们最直接的方式找到某个状态的片段,而且在之后的维护和调试过程中,也可以非常方便的管理和维护。
Getters
类似于Computed计算属性用法,多个组件需要调用经过变化的数据时使用。
- 第一个参数:state
- 第二个参数:调用getter本身
- 通过返回函数来实现getter传参
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
students: [
{id: 110, name: 'why', age: 18},
{id: 111, name: 'kobe', age: 24},
{id: 112, name: 'james', age: 30},
{id: 113, name: 'curry', age: 10}
]
},
Getters: {
// 接收state作为第一个参数
more20age(state) {
return state.students.filter(s => s.age > 20)
}
// Getter 也可以接受其他 getter 作为第二个参数
more20agecount(state, getters) {
return getters.more20age.length
// return state.students.filter(s => s.age > 20).length
}
// 通过让 getter 返回一个函数,来实现给 getter 传参(使用:moreage(20))
moreage(state) {
return function(age) {
return state.students.filter(s => s.age > age)
}
// return age => {
// return state.students.filter(s => s.age > age)
// }
}
}
})
Mutation
Mutation状态更新
mutation的定义方式
// store/index.js
mutations: {
increment(state) {
...
}
}
通过mutation更新
// App.vue
addition() {
this.$store.commit("increment")
}
Mutation传递参数
传递的额外参数也称为mutation的载荷(payload)
- 传递普通参数
// store/index.js
mutation: {
increment(state, count) {
state.count += count
}
}
// App.vue
addition() {
this.$store.commit('increment', 5)
}
- 传递对象参数
// store/index.js
mutation: {
addStudent(state, stu) {
state.students.push(stu)
}
}
// App.vue
addStudent() {
const stu = { id: 1, name: Never, age: 24 }
this.$store.commit('addStudent', stu)
}
Mutation提交风格
普通方式:
this.$store.commit('incrementCount', count)对象风格方式:将整个提交的对象作为payload使用
// App.vue this.$store.commit({ type: 'incrementCount', count }) // store/index.js // 此时payload:{ type: 'incrementCount', count: count} mutation: { incrementCount(state, payload) { state.count += payload.count } }
Action
- 用来代替Mutation进行异步操作的,同样也支持payload。
基本使用
- 通过dispatch分发到Action,再通过context进行commit提交到mutation。
// App.vue
methods: {
increment() {
// 传递一个对象参数的payload
this.$store.dispatch('increment', {count: 5})
}
}
// store/index.js
mutation: {
increment(state, payload) {
state.count += payload.count
}
},
actions: {
// 这里的参数是context上下文
increment(context, payload) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('increment', payload)
}, 5000)
}
}
一般将异步操作放在Promise中
// store/index.js
actions: {
increment(context) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('increment')
resolve()
})
})
}
}
// App.vue
methods: {
increment() {
this.$store.dispatch('increment').then(res => {
console.log("返回一个Actions成功的回调!")
})
}
}
Module
const moduleA = {
state: () => ({ ... }),
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: () => ({ ... }),
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = createStore({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
$store.state.a.xxx // -> moduleA 的状态
$store.state.b.xxx // -> moduleB 的状态
对于模块内部的 getter,就会有第三个参数为根节点状态rootState:
const moduleA = {
// ...
getters: {
fullname(state) {
return state.name + 'aaa'
},
fullname2(state, getters) {
return getters.fullname + 'bbb'
},
fullname3(state, getters, rootState) {
// rootState.name为根节点中state中的name
return getters.fullname2 + rootState.name
}
}
}
项目组织结构

Loading...